Magnetic materials are composed of areas called “magnetic domains” which are randomly oriented small magnets. In the presence of an MMF source like a wire of N turns carrying I, the magnetic domains align themselves with the magnetic field.
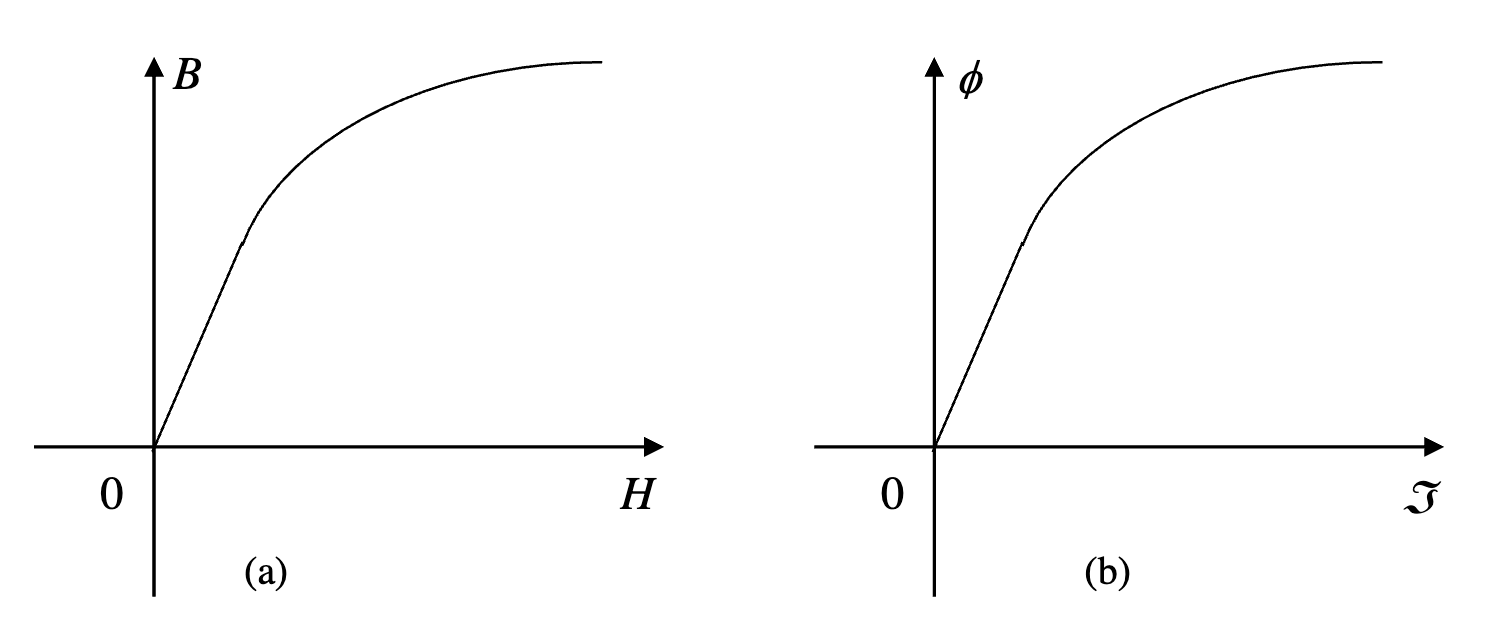
BH Curve
The BH curve of a non-magnetic material is linear with a very small slope.
The BH curve of a ferromagnetic material is nonlinear with a large slope.
In the BH curve of a ferromagnetic material, three distinct regions can be identified:
- Linear region (large and constant mu)
- Saturation region (increasing H does not really increase B)
- The knee of saturation (The region between 1 and 2)
Example Curve
Hysteresis
Exciting a core to create a permanent magnetic is caused by Hysteresis
Eddy Current Loss
See Eddy Currents
Power Loss
Where:
- = constant
- V = volume of magnetic material
- = peak value of magnetic flux density
The total core loss is obtained by summing these two losses.