From MTE 321
Machine and Mechanisms
A machine uses mechanisms to aid in its function to produce desired motion
A machine is a collection of mechanisms arranged to transmit forces and do work
Kinematics: The study of the geometric aspects of motion.
Position
Calculating the position vector
We calculate position using a vector with some origin as a reference. We’ve been doing this for years so not much to say here, I’ll give the equations anyways…
We can also transform this polar representation to rectangular form like how we do in Complex Numbers.
Displacement
Displacement
The difference between an initial and final position of a point (change in position).
The magnitude of displacement is path length.
Pure Translation
- Is rectilinear or curvilinear:
- All points moving in straight or curved lines
Pure Rotation
- All particles of a body move along circular paths in planes perpendicular to the axis of rotation
General Plane Motion
- The body undergoes translation and rotation
- Translation occurs within a plane and rotation happens perpendicular to the axis of rotation
Degrees of Freedom
- The number of independent parameters needed to define a systems position in space
Linkages
- The basic building blocks of all mechanisms
- Made of links with joints and nodes
Joints
- Joins are a connection between two or more nodes at the nodes
- Joints are classified by:
- The type of contact between elements
- Number of degrees of freedom
- Physical closure
- Number of links joined
- The degree of freedom is one less than the number of links joined
Crank
- A link that makes a complete revolution and is pivoted to the ground
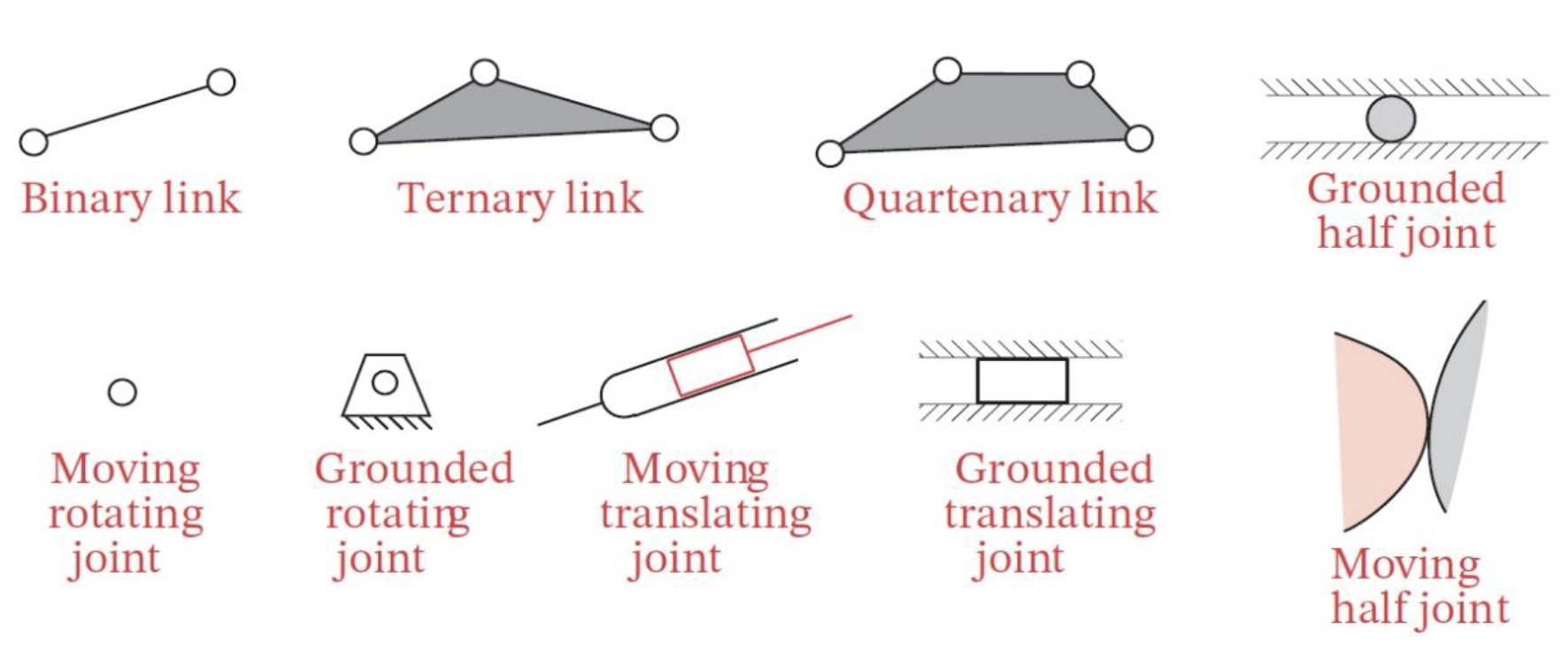
Drawing Kinematic Diagrams
- Identify frame
- Identify other links
- Identify joints and types of joints
- Identify points of interest