Generation of EMF
Two mechanisms for generating EMF from a magnetic field
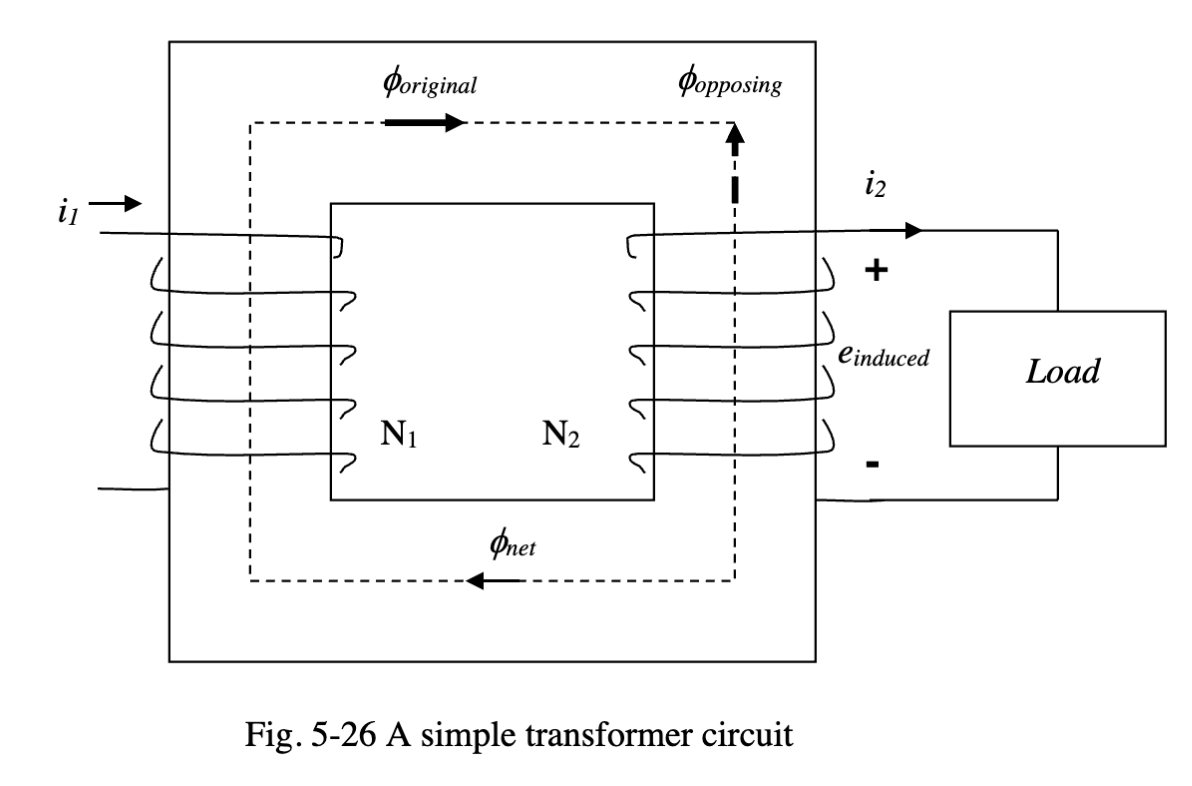
Faradays Law
When a flux passes through a coil of wire, an emf will be produced in each turn of wire which is also proportional to the rate of change of the flux passing through the turns of wire with respect to time.
If the sae flux passes through all N turns
Where LAMBDA is the flux linkage and the sign dictates polarity
Lenz’s Law
The polarity of an induced voltage will produce a NEW flux that opposes change in the original flux (the flux that generated it) with respect to time.
Applications
- Transformers
- Synchronous Generators
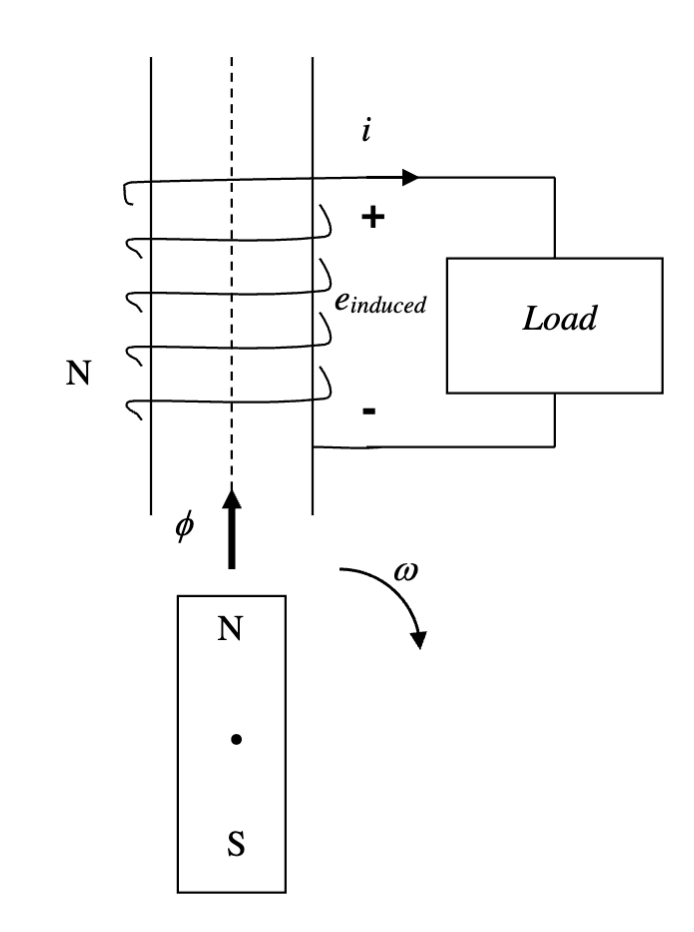
In Electric Machines Involving a Conductor and Magnetic Field
For an emf induced in a conductor of length l, moving at velocity v, in the presence of magnetic field B:
To maximize v x B and therefore, the magnitude of the emf, v is always designed perpendicular to B
This is because…
Furthermore, v X B is also designed collinear to l to maximize the dot product
This is because…
Direction of emf
The direction of emf can be found using the right hand rule (v X B)
For more on Power generation, see DC Machines