High level overview
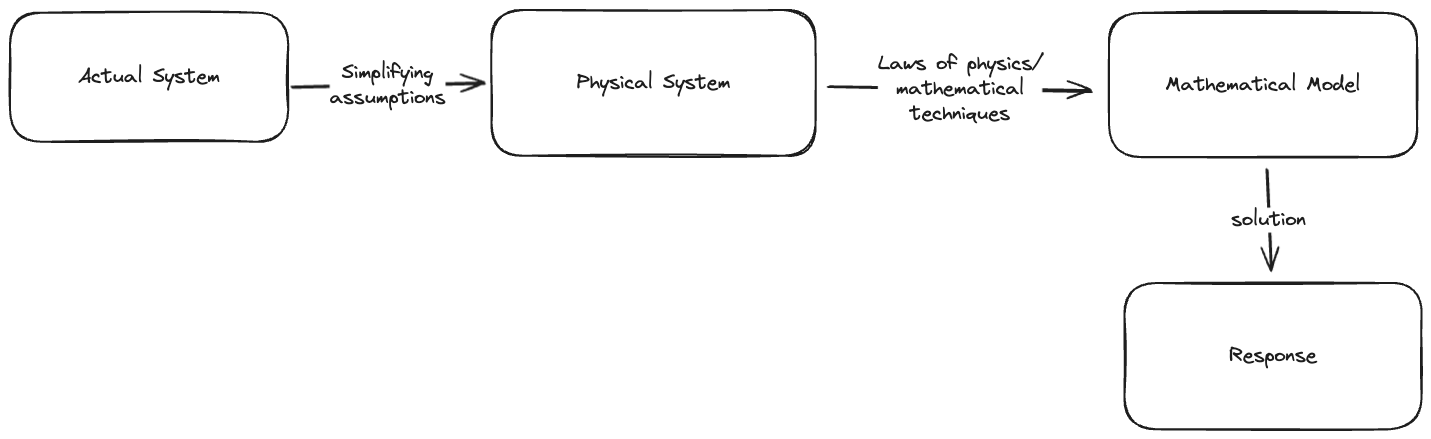
Definitions
Subconcepts
Modelling Mechanical Systems
Modeling of mechanical systems are fundamentally just making use of the fundemental law of physics (Newtons 2nd Law)
You may need a variable for a massless node if a distance is taken from that point.
Note
When making equations of dynamic systems (equations of motion), we leave everything in derivatives when simplifying (get rid of integration)
Mechanical Systems
General Procedure
- Draw FBDs
- Apply Newtons 2nd Law
- Simplify as needed
- Typical elements include Spring Elements and Damped Elements
Electrical Systems
General Procedure
- Identify nodes and voltages using nodal analysis
- Apply KVL and KCL and simplify as needed
- Typical electrical elements include these Impedance elements from Circuits Review
Electromechanical Systems
Thermal Systems
Fluid Systems
- Uses Fluid Systems
This seems to follow “making equations of motion” from SYDE 351 - Systems Models 1
There is also the concept of Equivalent Mass and Inertia (i.e equivalent inertia seen by a motor through the gears)