Meassuring Firm Performance
- The Balance Sheet: is a snapshot of a firm’s financial position at a particular point in time (normally the last day of accounting period). It summarizes assets, liabilities and owners’ equity.
- The Income Statement: summarizes revenues and expenses over a period of time. (revenues, expenses, profits before taxes, taxes paid and profits after taxes)
- Financial Performance ratios (Key performance indicators)
The Balance Sheet
- Every organization has assets and liabilities Assets
- Assets are items to which the organization has legal title
- Current assets can be converted into cash within 1 year
- Fixed assets have a life greater than 1 year Liabillities
- Liabilities: debt owed (suppliers, employees, government)
- Current Liabilities debt normally paid within a year (accounts payable, taxes, wages, bank loan, …)
- Long-term liabilities debt normally paid beyond current year Owners Equity
- Owners’ Equity: The difference between assets and liabilities is a means of measuring what the organization is worth – it’s equity:
- Owners’ equity often appears as two components in a balance sheet:
- Stock: par value per share, also known as nominal or original value, is the face value of a bond or the value of a stock certificate, as stated in the corporate charter
- Retained earnings: the amount of net income left over for the business after it has paid out dividends to its shareholders
The Income Statement
- Income Statement summarizes revenues and expenses over a specified accounting period (Month, quarter, and year)
- Major components: Revenues, Expenses, Profits
- Revenues: from sales of goods/services
- Expenses: cost of goods sold, rent, insurance, wages, depreciation
- Income or profit before taxes: Revenues – Expenses
- Net income (profit): Income (profit) before taxes – taxes
Estimated Values in Financial Statements
- Financial statements are often estimated: they may not reflect market values
- Assets are valued on the basis of their cost (book value)
- Land is listed at the price paid - not its market value
- Plant and equipment is listed at the price paid less accumulated depreciation
- Depreciation on equipment computed using a depreciation model
- Stock or Shares are listed at par value (issue price)
- Finished goods inventory – manufacturing cost
- Most firms include their accounting methods/assumptions
- within periodic reports to aid interpretation of statements
Financial Performance Ratios
- Decision makers (inside and outside) need to know general performance of a firm
- Balance sheet/income statements are used for assessment
- Financial Ratio Analysis : key performance indicators
- These performance measures are financial ratios calculated from items on the income statement and balance sheet.
- In interpreting ratios, analysts should calculate the ratios over a number of periods to do a trend analysis
- Ratios should also be compared to industry standards
- Industry standards routinely published by commercial and government websites/publications (Statistics Canada)
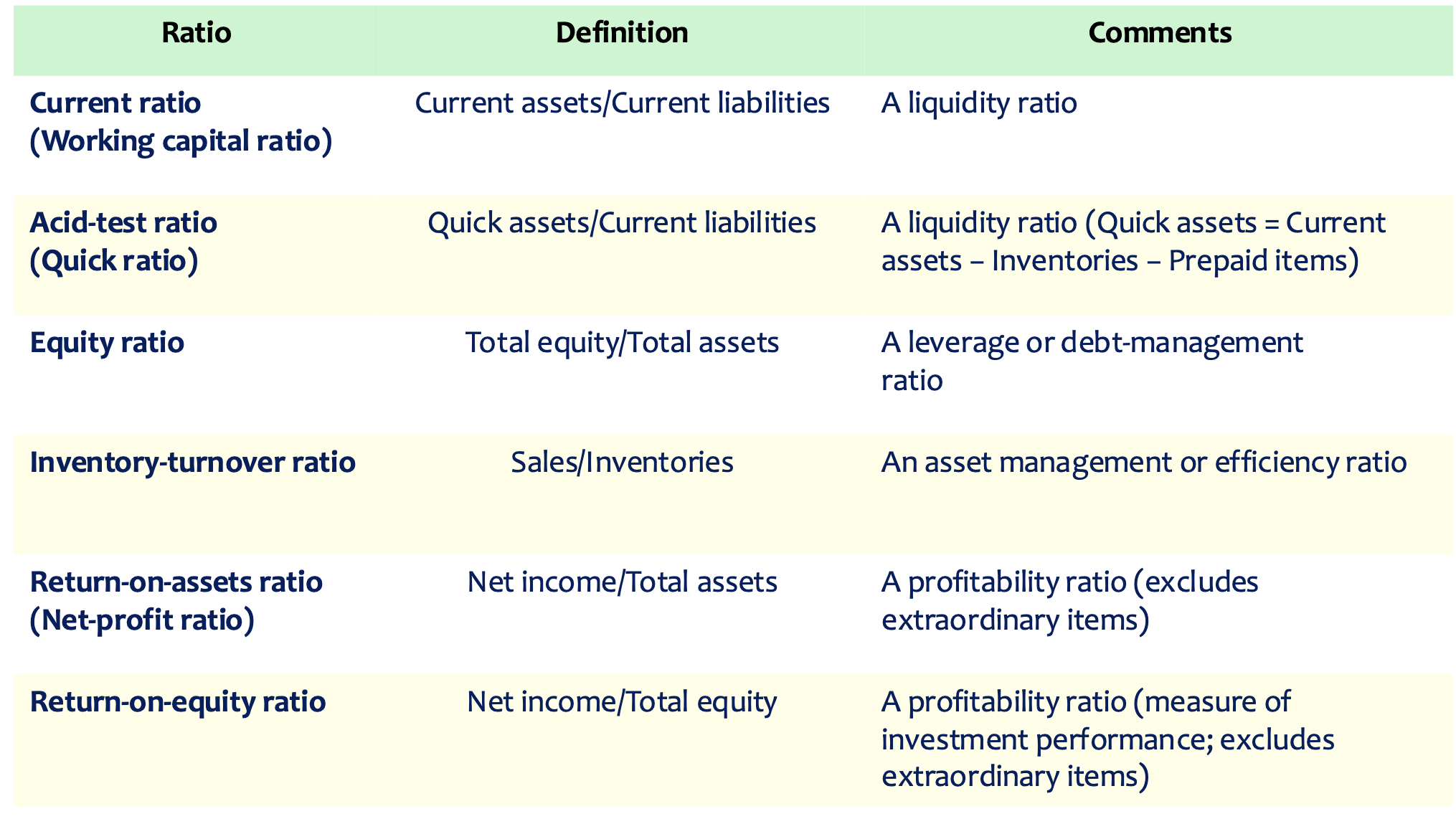
Financial Ratios
- Liquidity ratios: firm’s ability to meet short term financial obligations
- Company’s net reserve of cash and assets that easily can be converted to cash is called working capital.
- Working capital = current assets − current liabilities
- The adequacy of working capital is measured with two ratios:
- Current ratio
- Acid-test ratio (Quick ratio)
- A current ratio of 2+ is adequate
-
- Where quick assets are assets that are quickly convertible to cash
- Cash, accounts receivable, notes receivable, temporary investments in the market
- Inventory is not a quick asset
- An acid-test > 1 is adequate
- Where quick assets are assets that are quickly convertible to cash
- Debt Management Ratios: the extend to which a firm relies on debt for its operations
- : this is a measure of financial strength
- Debt ratio < 0.2 or less indicates sound financial condition
-
- The smaller the ratio, the more dependent a firm on debt and the higher risk of not being able to manage debt
- Comparison to industry norms/trend analysis necessary
- Efficiency Ratios: assess efficiency of use of its assets
-
- The total sale in a period divided by the value of average inventory level at the same period by the average selling price
- A higher ratio points to Strong sales and a lower ratio to weak sales
-
- Profitability Ratios: How productively assets have been employed in producing a profit?
Business Plan
A 3-5 year road map of a business
- Outlines operating, marketing, financial and HR status and intensions
- Identifies the nature and feasibility of the business considering financing options and forecasts cash flows
- Drafting a good BP is an essential step in starting a business
- Balance sheets, income statements and financial ratios are used in a BP to analuze the financial status of the company
Aspects of a Business Plan
- Executive summary
- Convinces investors to read further
- Primarily convinces reader of future success
- Features the mission statement, provided products and services, overall financial health, future plans
- Company Description
- High level overview of company and operations
- Products / services and market needs
- Company HR capabilities
- Competitive advantages of the company
- Market Analysis / Future Outlook
- Description of industry and growth plans of company
- Market demand: discussion of target market
- Future trends: customer demand, technology and market share
- Market share: present / future share compared to competitors
- Weaknesses and strengths
- IT and technology advances
- Geographical location
- Financial situation
- Experience and human factors
- Pricing, revenue and cash flow predictions
- Regulatory environment
- Management and Organization
- Explanation of structure of business in detail
- sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation
- Key corporate employee information provided
- Experience, education, qualifications
- Functional groups, corporate structure, job titles
- How this structure suits corporate mission and future growth
- Explanation of structure of business in detail
- Funding Requirements
- Discussion of where the funding will originate
- Owners and investors
- Banks and other financial institutions
- How company will attract investors for new projects or expansion
- Discussion of where the funding will originate
- Sales and Marketing
- Strategies to penetrate target markets
- Creation / maintaining of customers
- Recognition and fulfillment of needs
- Communication mechanisms (surveys, advertisements) promotions