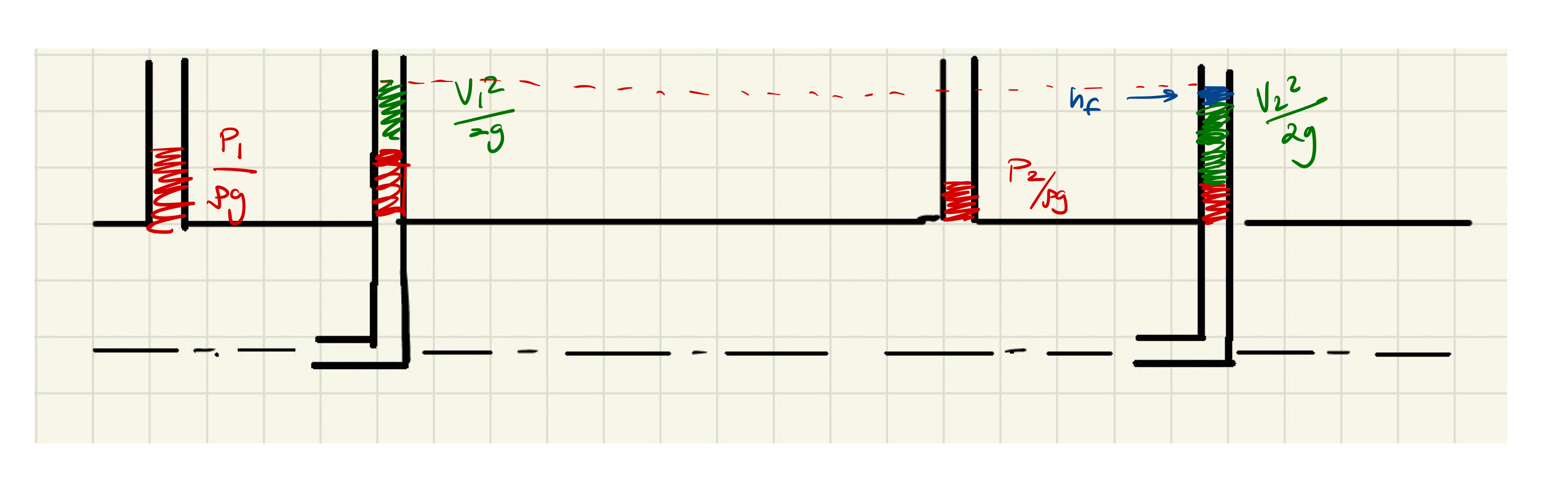
Definition
The point where velocity of fluid is brought to zero by means other than friction
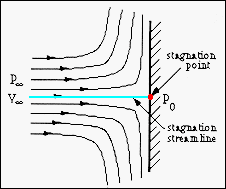
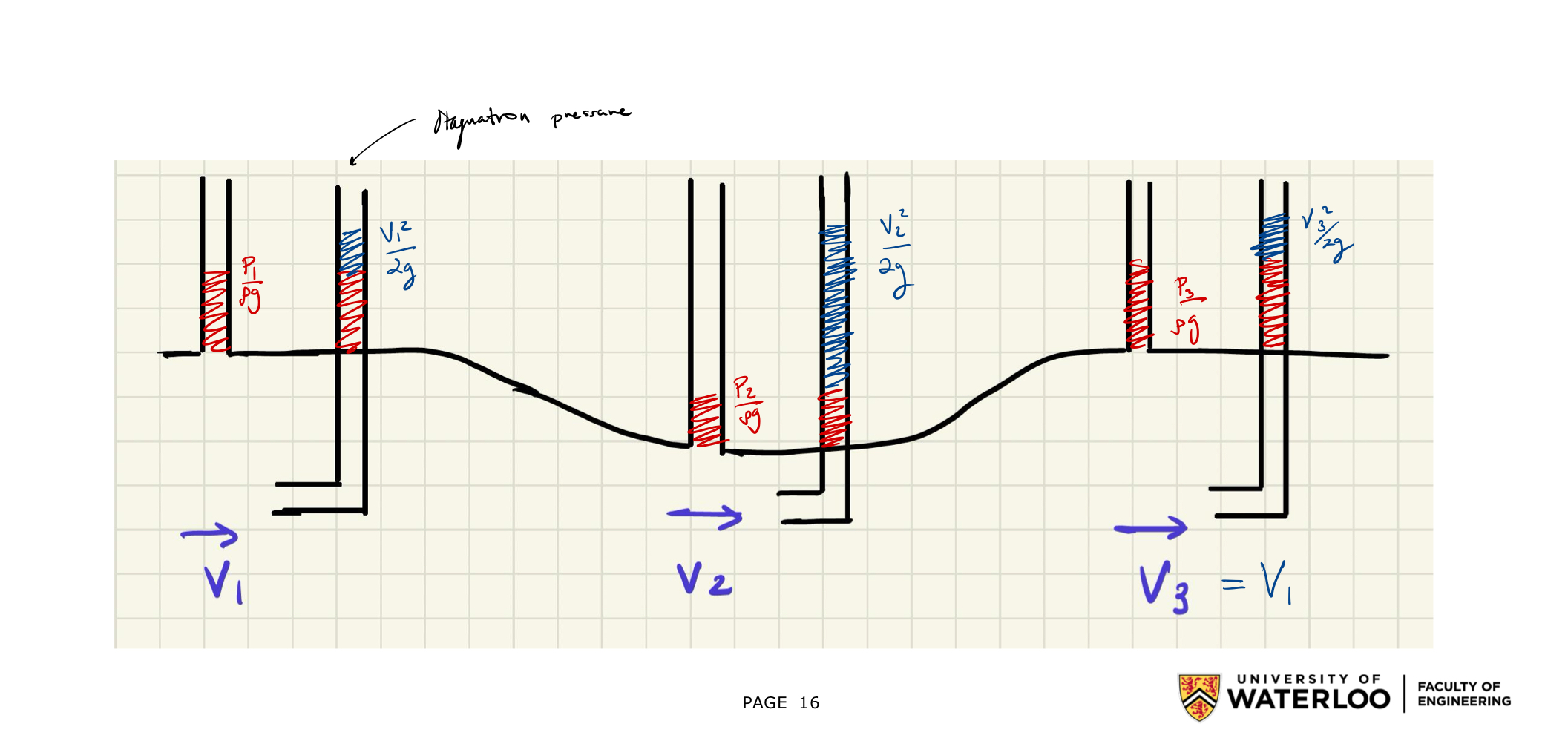
The stagnation pressure is defined as where in the figure above is
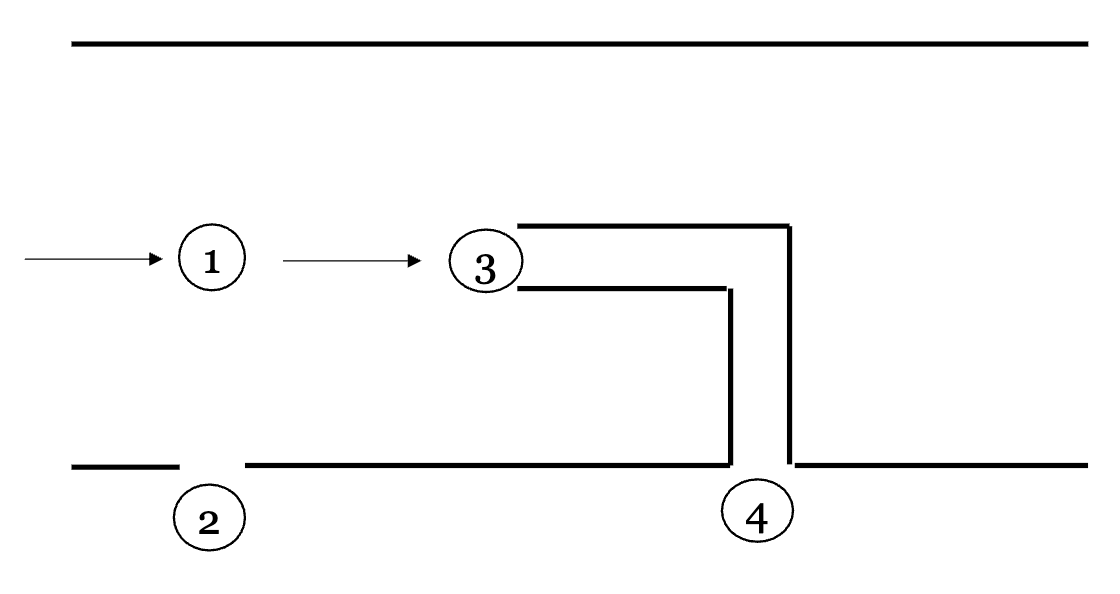
Pitot Tubes
- Uses stagnation pressure to measure flow velocity
- Here, p1=p2 and p3=p4 and within the tube the air is still
- Using a streamline from 1 → 3, we can find the velocity at 1… where the height components here cancel and is the stagnation point so it is 0
Venturi
Relevant in these types of questions…
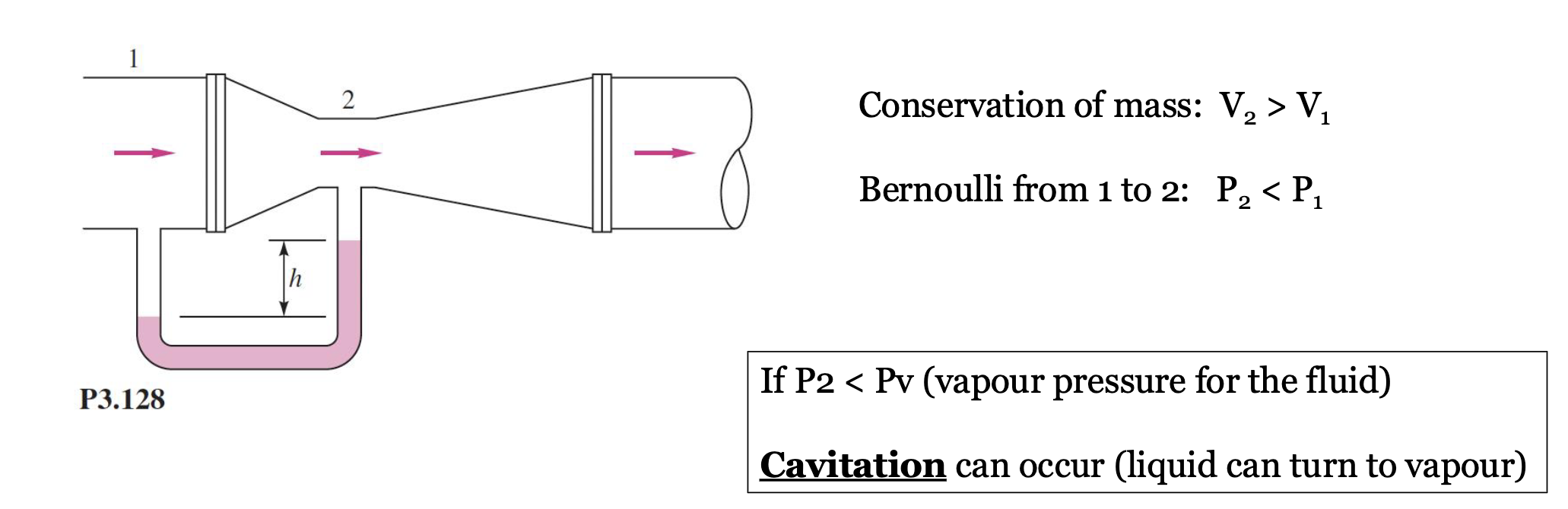
Vapour Pressure and Cavitation
- Surface tension → molecules at a surface experience intermolecular forces
- A random number of the molecules can break free form these forces → evaporation
- Some molecules will return to the liquid → condensation
- Equilibrium is when evaporation rate = condensation rate
- At equilibrium, the pressure in the vapour phase is called vapour pressure
- We want to avoid cavitation
Head Loss
Sudden Expansion
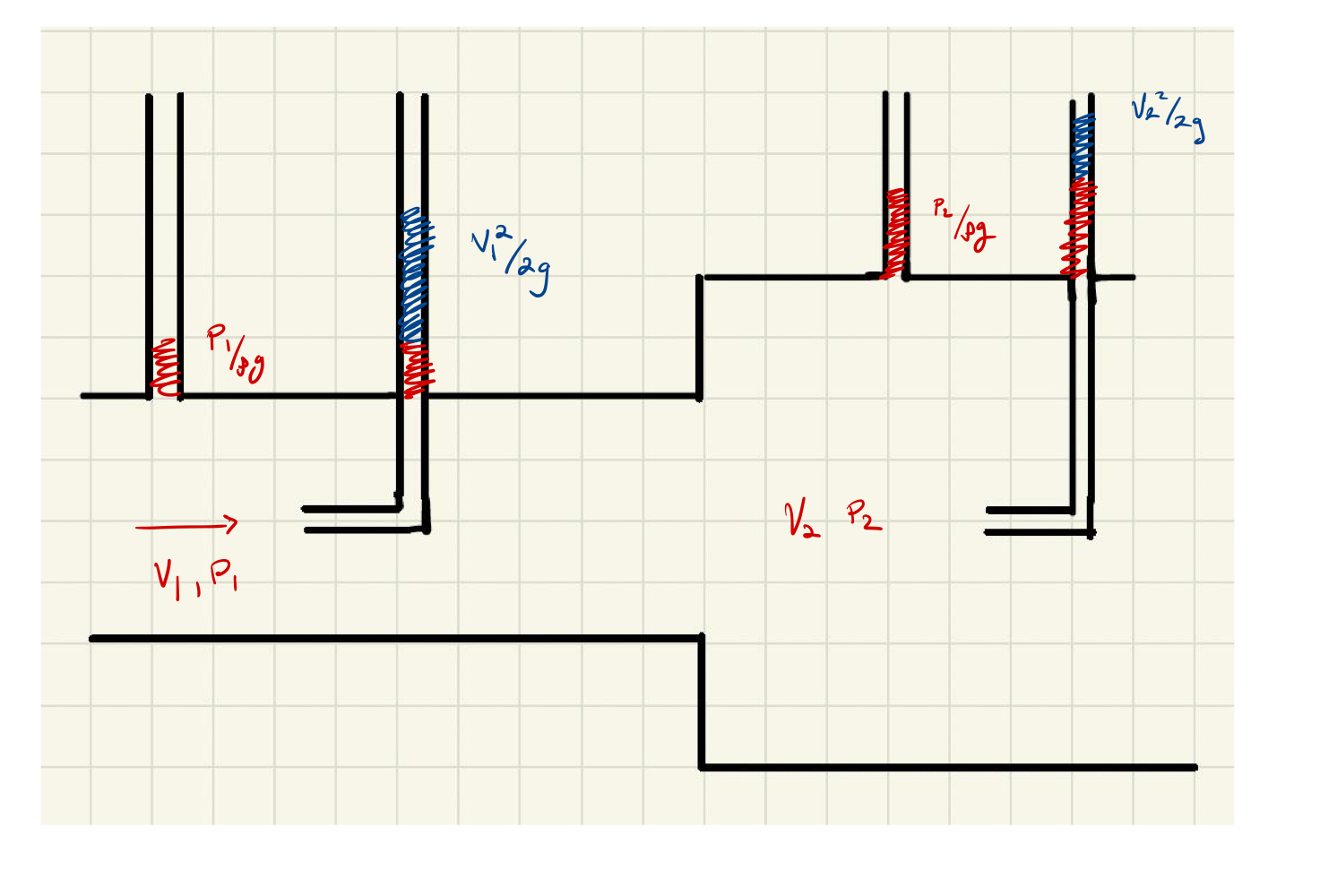
Long Pipe