Summary
- Money has value over time
- Evaluating future costs and benefits now needs to consider time value of money
Interest and Interest Rates
- Lending money should be compensated
- Since the lenders loose the opportunity to invest the money they rent out, they should get additional compensation so it acts in the same way
- Therefore, the compensation of loaning money is the interest payment
- I.e instead of rent for an apartment, we charge interest
This can be represented as…
- → interest rate
- → present worth
- F → future worth of P
Alternatively, over n years your interest can…
compound (using the Compound Effect)
or be simple
Simple Interest Rate
Not compounding, interest amounts are not considered for calculating interest in the future (the initial value is called the principle investment)
You can find the compound interest amount through
Effective and Nominal Interest Rates
- : is the nominal rate started for a period (nominal means 1 year)
- : is the number of equal compounding periods
- : is the effective interest rate
- : is the interest rate for sub-periods In this case:
Effective Interest Rate
gives the same future amount, F, over the full period as when sub-period interest rate is compounded over sub-periods
Modifying the period
We typically need to modify what is based on the problem. For example if we compound semi annually, our new will be
Continuous Compounding
Continuous compounding has no end in sight.
This is often not used, discrete compounding is the norm.
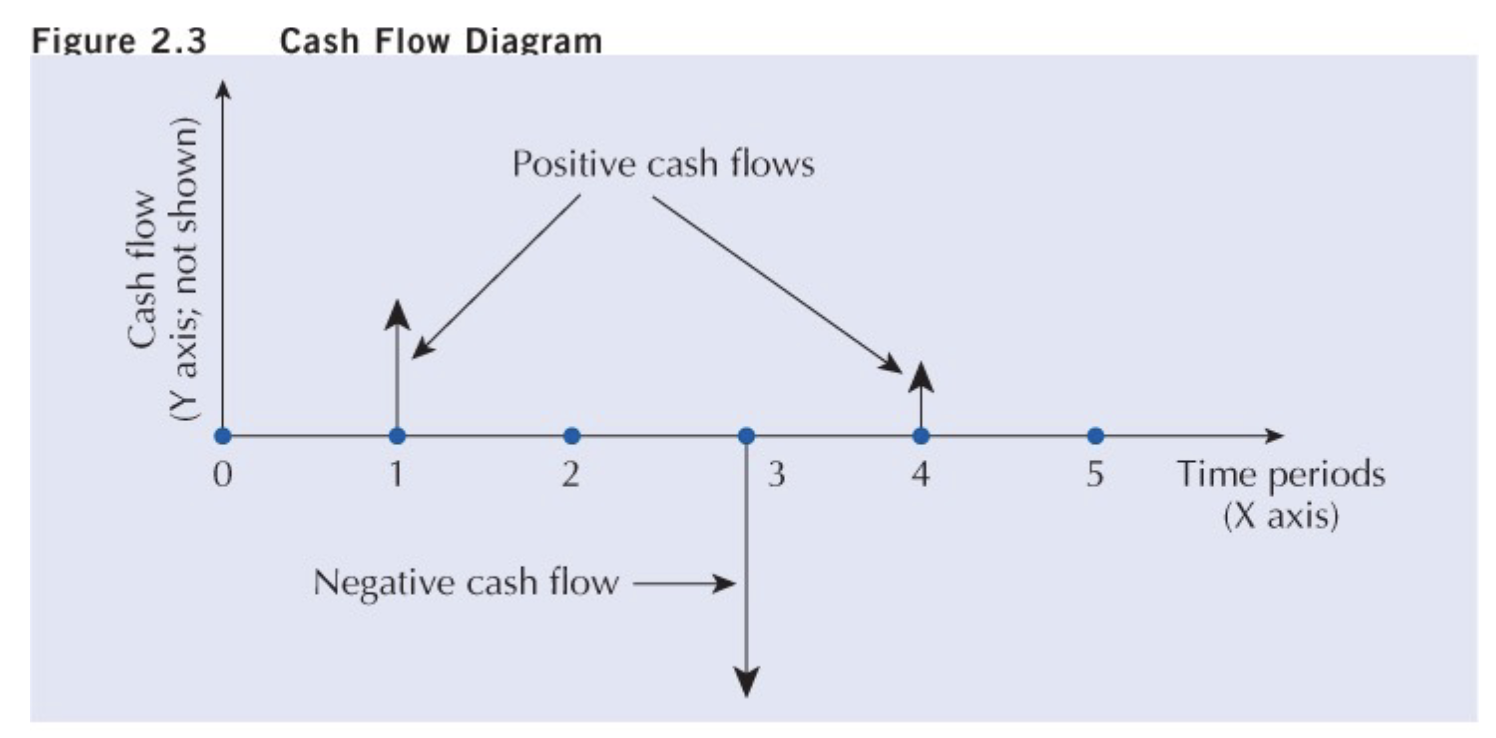
Cash Flow Diagrams
This is a graphical summary of the timing and magnitude of cash flows.
Depreciation
Assets loose value over time for typically the following reasons…
- Use related physical loss
- Measured in units of production
- Time related physical loss
- Measured in units of time
- Functional loss
- Value can be lost without physical changes
- Style change in cars can cause depreciation in an owned car
- Legislative changes
Value of an Asset
- Depreciation models are used to estimate the value of an asset at any given time
- Market Value
- The actual value of the asset that can be solved for in an open market
- Book Value
- The value of an asset calculated from a depreciation model for accounting purposes
- Salvage Value
- Actual or estimated value at the end of useful life
- Scrap Value
- Actual or estimated value at the end of its life
Depreciation Methods
Straight Line
Assumes rate of loss of asset’s value is constant over its life
- P = purchase price
- S = salvage value at the end of N periods
- N = Useful life of asset
This is modelled as… Depreciation
Book Value
Accumulated Depreciation
Declining-Balance Depreciation
- Models loss in value of an asset in a period as a constant proportion of the asset’s current value
- Book Value here is
- Book value at the end of period n is
- Depreciation in period n is
- The relationship between the current value (P), salvage value (S) at period n from now when the salvage value and useful lifetime are known
- If the salvage value is known… otherwise if the salvage value is not known,
Equivalence
- Engineering economics involve costs and benefits at different times
- Comparison analysis is accurate when certain values at different times are equivalent
Equivalence
Equivalence means the value of a cost at one time is equivalent of a related benefit at a different time.
The three concepts of equivalence are:
- Mathematical Equivalence
- Using the relationship to exchange P dollars for F dollars
- Decisional Equivalence
- P dollars now is indifferent from F dollars N periods from now
- Market Equivalence
- Exchanging different cash flows in a market at zero cost.
- i.e Lending out 500/month over 36 months for $3000 profit
Lecture Example
The example given in the lecture, was taking different dollar amounts at different points in time and converting them all to the same time for a direct comparison using…
.The lecture example has a negative 2000 at time 0 and then gains of 1000, x, and 1200 at times 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The example then sums the three equivalent values and sets them equal to 2000 (since we need to balance everything) and then we can solve for x